The Station

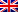
The station is a remote site of Abruzzo Astronomical Observatory located in the heart of the Appennino, in the Middle Italy, 2200 m above the sealevel. Clic here to see how to reach Campo Imperatore (AQ).
The darkness of the sky is very good, especially when the thermal inversion level lies below 2000 m a.s.l.. In this case, the clouds layer shields the Observatory from unwanted light coming from the valleys around. However, "darkness" is a relative concept in the near-infrared: indeed, the sky brightness is related primarily to the water vapour content of the atmosphere, rather than to the scatter of light by atmospheric aerosols. The typical sky brightness at Campo Imperatore amounts to 15.5, 14.5 and 11.5 mag/arcsec2 in the J, H and K band, respectively.
The weather conditions are good but not excellent: on average, the 50 % of the nights is clear. However it should be noticed that this Observatory was built in the 1950s, when the site testing was not yet a science.
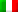
The AZT-24 telescope
The AZT-24 is a 108 cm-aperture telescope located in the East dome of the Campo Imperatore Observatory.
Built by LOMO optical workshops for Pulkovo Observatory (St. Petersburg, Russia), it has been moved to Italy on 1995 and installed in its current location on 1997, in the framework of the SWIRT Project .
The telescope is equipped with the near-infrared camera SWIRCAM (1.1 - 2.5 μm ), provided by the Teramo Astronomical Observatory.
It is devoted to the search for extragalactic Supernovae in the near-infrared (SWIRT Project), and studies of stellar variability, galaxy luminosity, active galactic nuclei and minor bodies of the Solar System.
The AZT-24 is currently the only telescope on the italian ground to be equipped with near-infrared instrumentation.
| Optical design | Ritchey-Chrétien with optional corrector | ||||||
| Flat focal plane field size | 20' = 46 mm ( 84' = 195 mm with corrector ) | ||||||
| Primary mirror | diameter focal length |
1100 mm 4553 mm |
|||||
| Primary mirror weight | net in the cell |
280 Kg 1820 Kg |
|||||
| Secondary mirror | diameter | 590 mm (Cassegrain focus) | |||||
| Distance from primary mirror | 2605.5 mm (2611.0 mm with corrector) | ||||||
| Cassegrain equivalent focal length | 7971 mm (7965 mm with corrector) | ||||||
| Telescope frame type | equatorial (German) | ||||||
| Psf parameters @632.8 nm | on axis | 74% total 66% total |
light | energy | in 0''.52 circle in 0''.31 circle |
||
| off axis | 46% total 39% total |
in 0''.52 circle in 0''.31 circle |
|||||
| (These figures correspond to FWHM about 0''.25 on axis and 0''.30 at the field edge) | |||||||
| Mirror roughness | λ/30 rms | ||||||
| Focal plane offset from the instrumental flange | 60.2 mm (61.2 mm with corrector) | ||||||
| Telescope movements | DC motors | ||||||
| Pointing equipment | absolute encoders | ||||||
| resolution: | about 10'' (mechanical precision only) | ||||||
| speed: | rough guidance 75' per second exact guidance 15''-16'' per second |
||||||
| Total telescope weight | 32 tons (moving part 24 tons) | ||||||
Note: In order to use the infrared camera, a 45° tertiary plane mirror ( M3) is currently installed which deflects at right angle the optical beam toward the detector.
-- See the AZT-24 Image gallery --